Insulation is the most important way to reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Depending on your home, insulation can be quick to retro fit without major renovations, but should certainly be included in new builds or during major renovations, when it is easier to install.
What is insulation?
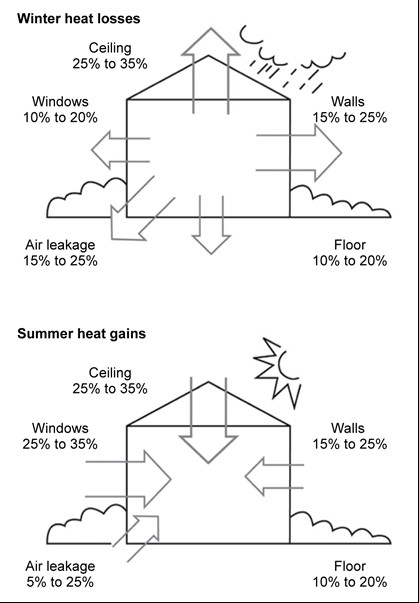
All materials allow heat to pass through them. Insulation reduces the amount of heat transferred through building materials like brick, plasterboard, glass and metal by providing substantial resistance to heat flow either in to or out of a building. This means that the need for heating and cooling is minimised. Ideally, insulation should be installed in the ceiling, walls and floors of your home to create a sealed envelope which acts like a thermos in winter to keep heat inside, and like an esky in summer, to keep heat out.
Benefits of insulation
Insulation is the cornerstone of an energy efficient home. Insulation is also the most cost-effective way to improve the energy efficiency and comfort of your home. A fully insulated home compared to a non-insulated home can reduce the cost of heating and cooling a home by around 40 to 50%. Adding bulk insulation, either to new or existing homes creates a more comfortable home year round, virtually eliminates condensation on walls and ceilings and can pay for itself in around five to six years.
Key points
- Insulation is a material that slows or prevents the flow of heat.
- Insulation is a key part of any passive designed home, helping to keep heat inside the home in winter and outside the home in summer.
- The performance of any insulation product – how well it resists heat flow – is know as its R value. The higher the R value, the higher the level of insulation.
- The ‘total R value’ adds together the R value of the various components of a roof, ceiling, wall or floor, including the insulation.
- The type and R value of insulation that is best suited to your home will depend on your climate and construction type.
- There are a wide range of insulation products. Bulk insulation uses air pockets within a thick material to slow the flow of heat. Reflective insulation reflects heat back to where it came from, and if double sided does not re-radiate heat on the opposite side. Composite insulation combines bulk insulation with a reflective surface.
- All insulation should be installed carefully following the product specifications, to minimise the risk of condensation or fire.
- Thermal bridges’ are pathways for heat transfer through components of the floor, walls or roof. They need to be identified and insulated to prevent heat flow and condensation risk.
- Some types of insulation should be installed by a professional, while some you can do yourself. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.